| SD-WAN offers networks improved WAN management with dynamic routing, cost savings and integrated security, outperforming traditional WANs for both flexibility and efficiency. |
In 2024, we’re all aware that SD-WAN has transformed WAN architecture. SD-WAN vendors are now viewed as a necessity for any organisation requiring secure public Cloud access across any combination of transport services, including leased lines, 4G/5G LTE, and broadband Internet connections. By decoupling the network hardware from the control mechanism, SD-WAN is capable of improving productivity and reducing costs compared to legacy WAN solutions.
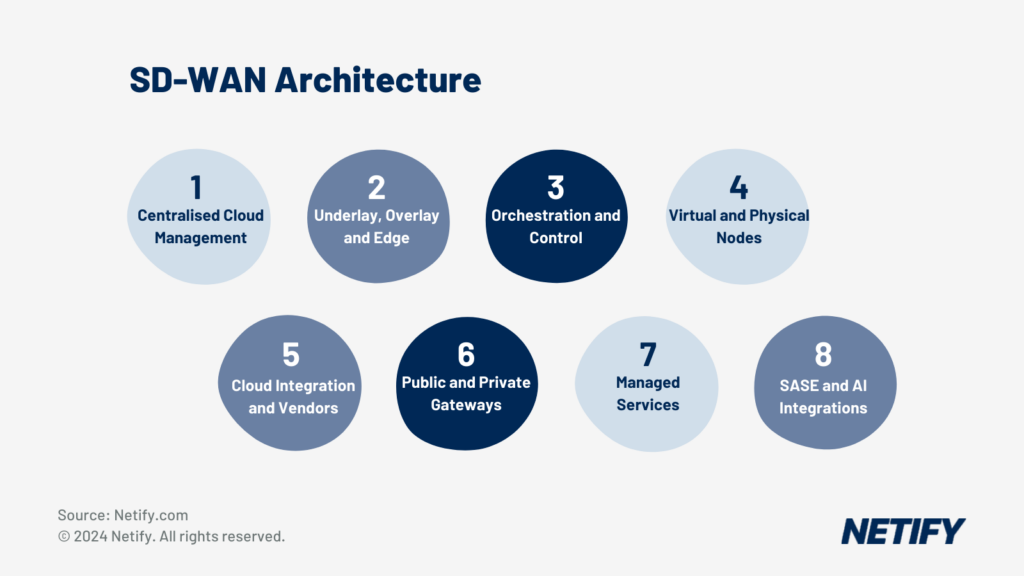
- SD-WAN Architecture
The architecture of SD-WAN is designed to simplify management, and drive digital transformation initiatives by optimising application performance and enhancing user experience across SaaS and public cloud services. Although SD-WAN is often researched in isolation, the technology is actually a component of Service Edge (SASE) architecture. SASE combines network security functions with SD-WAN capabilities to support networking and security requirements across most Enterprise businesses.
In short, SD-WAN architecture serves as an enabler for enterprise agility, cost reduction, and improved cloud application performance.
Centralised Cloud Management
The adoption of a centralised cloud management approach signified the biggest evolution across SD-WAN managed services. IT teams no longer had to wait days for simple change requests to be actioned by service providers, moves or changes are now performed in real-time.
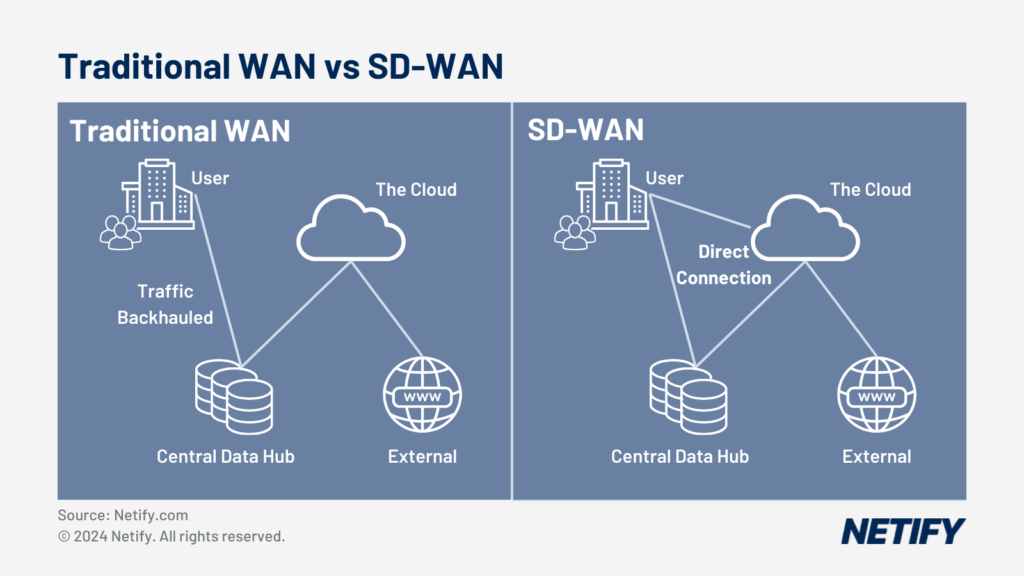
- Traditional WAN vs SD-WAN
With SD-WAN, centralised cloud management is typically delivered via a unified control interface, enabling administrators to understand network performance and trends, patch hardware as required, view security threats and make changes on a real-time basis.
Centralised management functions via a dedicated controller, which standardises network configurations and policies across branch-office locations and remote users. This approach ensures that changes in network behaviour or adjustments to policy are deployed across all users and locations instantaneously.
The primary benefits include:
SD-WAN Architecture Primary Benefits
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Feature | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:28 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:28 PM | Simplified Administrative Procedures | Centralised management removes the need for manual configuration at each branch, resulting in reduced operational complexity and the potential for human error. |
| 2 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:28 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:28 PM | Enhanced Application Performance | Real-time traffic steering, enabled by centralised management, optimises application delivery and ensures consistent performance even in diverse network conditions. |
| 3 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:28 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:28 PM | Augmented Network Security | Centralised cloud management can implement uniform security protocols quickly, improving the overall posture against cyber threats. |
| 4 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:28 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:28 PM | Orchestration of WAN Edge Devices | Centralised controllers can orchestrate edge devices to cater to dynamic traffic demands and cloud resource access, leading to optimisations in network agility and application accessibility. |
| Feature | Description |
The above strategic benefits are fundamental to businesses looking to harness the agility of cloud resources while maintaining control over their network infrastructure. The capability added by centralised SD-WAN management systems ensurer networks remain resilient and responsive to rapidly evolving requirements.
SD-WAN Underlay and Overlay
SD-WAN Underlay is the IP network reachability across branch-office and remote user locations, i.e. the connectivity. SD-WAN architecture is capable of supporting multiple WAN transport methods such as 4G, 5G, LTE, Broadband (Fibre to the Premises or FTTP), and leased lines. The underlay layer is vital as it forms the foundation upon which the SD-WAN architecture is structured.
In contrast, SD-WAN overlay refers to the SD-WAN network intelligence that is deployed and managed across the underlay network. The underlay is characterised by IPsec tunnels that connect sites together, enabling the encryption and delivery of data packets over the underlay infrastructure. This abstraction is key to understand – it demonstrates how SD-WAN architecture orchestrates a more efficient network through dynamic path selection that optimally routes traffic and services.
SD-WAN Architecture Underlay vs Overlay Comparison
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Aspect | Underlay | Overlay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:33 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:33 PM | Technology | Routers, switches and other physical devices | Virtual IPsec tunnels forming the SD-WAN Fabric |
| 2 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:33 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:33 PM | Function | Provides the basic infrastructure and IP reachability | Manages routing and optimises traffic across the underlay |
| 3 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:33 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:33 PM | Connectivity | 4G, 5G, LTE, Broadband (FTTP), leased lines, etc. | IP connections routed over the physical infrastructure |
| 4 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:33 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:33 PM | Relevance | Foundational layer for SD-WAN | Enables SD-WAN capabilities and dynamic, efficient routing |
| Aspect | Underlay | Overlay |
The above strategic benefits are fundamental to businesses looking to harness the agility of cloud resources while maintaining control over their network infrastructure. The capability added by centralised SD-WAN management systems ensurer networks remain resilient and responsive to rapidly evolving requirements.
SD-WAN Underlay and Overlay
SD-WAN Underlay is the IP network reachability across branch-office and remote user locations, i.e. the connectivity. SD-WAN architecture is capable of supporting multiple WAN transport methods such as 4G, 5G, LTE, Broadband (Fibre to the Premises or FTTP), and leased lines. The underlay layer is vital as it forms the foundation upon which the SD-WAN architecture is structured.
In contrast, SD-WAN overlay refers to the SD-WAN network intelligence that is deployed and managed across the underlay network. The underlay is characterised by IPsec tunnels that connect sites together, enabling the encryption and delivery of data packets over the underlay infrastructure. This abstraction is key to understand – it demonstrates how SD-WAN architecture orchestrates a more efficient network through dynamic path selection that optimally routes traffic and services.
The routing within the overlay enhances network performance and reliability through capability to solve the constraints presented by traditional WAN architectures. The overlay’s ability to optimise transport for services extends to varying forms of internet connections, and MPLS, VPLS or private circuits.
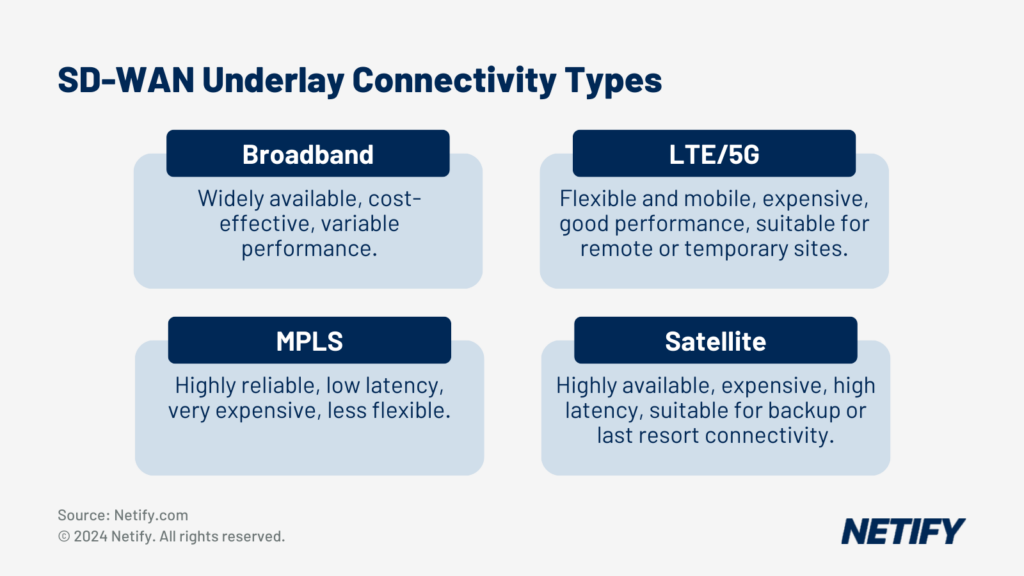
- SD-WAN Underlay Connectivity Types
SD-WAN Edge
The SD-WAN Edge defines the devices placed at the periphery of a network to handle the ingress and egress of traffic between the LAN and WAN.
SD-WAN Edge Functionality
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Functionality | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:34 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:34 PM | SD-WAN Edge Control | The SD-WAN edge enables secure and intelligent pathway control, which supports application performance and rapid provisioning. |
| 2 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:34 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:34 PM | Dynamic Routing | The SD-WAN Edge utilises dynamic routing protocols to select the optimal path, considering current network conditions to maintain performance and reduce latency. |
| 3 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:34 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:34 PM | Provisioning Options | The SD-WAN Edge can be provisioned as either a physical appliance or virtual instance. |
| Functionality | Description |
SD-WAN Edge Key Components
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Component | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:35 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:35 PM | Routing | Directs data across the network, choosing the best path based on the current conditions. |
| 2 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:35 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:35 PM | Security | Protects data integrity and confidentiality across the network. |
| 3 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:35 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:35 PM | Application-aware Policies | Allows the network to make decisions based on the type of application traffic. |
| 4 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:35 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:35 PM | WAN Optimisation | Improves data transfer efficiencies across wide area networks. |
| Component | Description |
The MEF Forum has outlined the SD-WAN Edge’s role in ensuring that consumer-grade broadband and other transport mechanisms provide service quality similar to that of a private circuit. In short, the MEF modular framework promotes performance even in the presence of multiple underlying transport links, such as MPLS, 4G/5G cellular, or broadband services.
Below is the typical WAN-Edge functions:
WAN Edge Functionality
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:36 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:36 PM | Traffic Shaping | Prioritises critical applications and manages bandwidth. |
| 2 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:36 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:36 PM | Security | Integrates features – i.e. firewall and threat prevention. |
| 3 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:36 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:36 PM | Path Selection | Dynamically selects the best path for each application flow. |
| 4 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:36 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:36 PM | Zero-Touch Provisioning | Streamlines device deployment with minimal manual intervention. |
| Function | Description |
SD-WAN Orchestrator
The Orchestrator plays a role in the management of SD-WAN, serving as a virtualised manager that oversees network traffic and the enforcement of policy and protocols determined by network administrators. The controller is used to enable centralised control over the network’s configuration and real-time monitoring.
Core Functions:
SD-WAN Orchestrator Core Functions
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Aspect | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:42 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:42 PM | Centralised Management | The orchestrator serves as the central point for configuring network devices and services, reducing the complexity involved in managing an extensive network. |
| 2 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:42 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:42 PM | Real-time Monitoring | It continuously monitors the network, allowing for prompt responses to changing conditions. |
| 3 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:42 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:42 PM | Data Flow Orchestration | Traffic is directed optimally across the network, balancing loads and prioritising applications as necessary. |
| 4 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:42 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:42 PM | Security Maintenance | Enforces security policies throughout the network, ensuring data protection and compliance with regulatory standards. |
| Aspect | Description |
The orchestrator works in collaboration with the SD-WAN Controller by enabling dynamic handling of network traffic. The dynamic management adjusts bandwidth demands and application requirements to ensure that user applications are perming across latency and jitter.
In SD-WAN deployments, the orchestrator analyses the priority level of applications, directing traffic effectively to maintain service levels and optimise the user experience. This includes routing decisions that can be made based on application, network congestion, or other custom-defined policies.
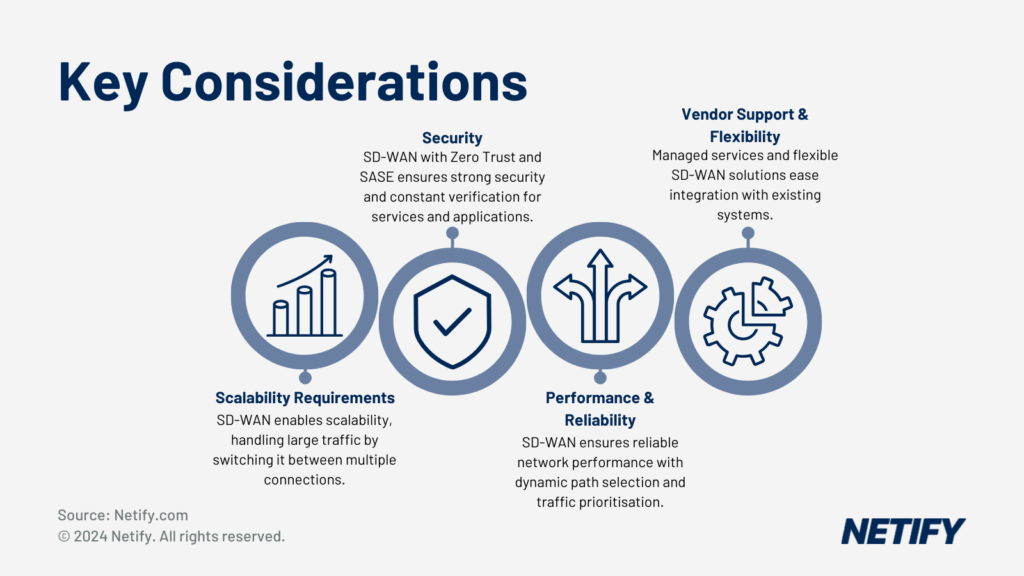
- Key Considerations for Large Enterprises when choosing an SD-WAN solution
For a detailed description of how the SD-WAN Orchestrator facilitates enterprise-wide network management, you may wish to read the VMware SD-WAN Orchestrator guide.
SD-WAN Controller
The SD-WAN Controller serves as the central management hub SD-WAN architecture, providing networking functions that underscore deployment speed and network performance. The controller operates by offering administrators a single software interface to manage and ‘control’ operation of the network.
In particular, one of the main roles of the SD-WAN Controller is to orchestrate network traffic to learn about real-time network conditions and to direct traffic accordingly. Listed below are key functions of the SD-WAN Controller:
SD-WAN Controller Functionality
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Aspect | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:45 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:45 PM | Centralised Management | Simplifying the complexity of managing large-scale networks by allowing a singular point of control. |
| 2 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:45 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:45 PM | Policy Administration | Enabling operators to define and manage network policies that align with business priorities. |
| 3 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:45 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:45 PM | Performance Monitoring | Collecting and analysing network performance data to facilitate informed decision-making. |
| 4 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:45 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 04:45 PM | Dynamic Routing | Adjusting traffic paths in response to network status and link performance to uphold service levels. |
| Aspect | Description |
The controller’s ability to execute policies and prioritise traffic is not just reactive but also predictive, taking into account various application requirements and network conditions. For enterprises, this capability translates into enhanced application performance and a more efficient utilisation of network resources.
The SD-WAN Controller integrates security protocols within the network. Good implementation ensures that not only is the network performance optimised, but the security posture is also implemented across all SASE elements.
The Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Solution Overview highlights the process of ongoing network management. This level of automation and centralisation is part of modern enterprises that rely on flexible network infrastructures.
Virtual or Physical Nodes
SD-WAN architecture is typically designed with either virtual or physical components classified as edge devices (see point 3).
The following table details the types of virtual or physical CPE which is used with SD-WAN:
Virtual & Physical WAN Appliances Comparison
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:11 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:11 AM | Physical SD-WAN Appliances | They are on-premises hardware units responsible for routing traffic between different network endpoints. The known advantage of dedicated hardware is that they are often built for network functions, potentially providing better performance and reliability |
| 2 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:11 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:11 AM | Virtual SD-WAN Appliances | Software instances that can be deployed on commodity hardware or within cloud infrastructure. They represent the virtualisation of SD-WAN functions and contribute significantly to network flexibility and scalability. Virtual appliances allow organisations |
| Type | Description |
Both virtual and physical SD-WAN nodes are responsible for the network overlay, essentially creating a managed network layer independent of the underlying transport links. They enforce defined policies to route traffic intelligently across the WAN, utilising broadband Internet, LTE/5G, or MPLS to establish high-performance connections for applications.
Virtual SD-WAN nodes offer Virtual Network Functions (VNFs), including security services and load balancing, which enable connections to emulate the quality of dedicated circuits. By deploying virtualised services, businesses can achieve operational efficiency compared to dedicated edge hardware with cost reductions.
In summary, the choice between virtual and physical SD-WAN nodes hinges on organisational requirements for performance, cost, scalability, and management. The ongoing evolution of network technology continues to shift the balance in favour of virtual solutions, characterised by adaptability and lower total cost of ownership.
Cloud Vendor Integration
SD-WAN’s integration with cloud vendors is now one of the most research subjects when IT decision makers compare vendors and service providers.
Cloud Vendor Integration Comparison
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Cloud Vendor | Integration and Features | Key Benefits | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:12 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:12 AM | Microsoft Azure | Azure SD-WAN connects branch sites to Azure via tunnels, allowing access to Azure workloads and automated interconnection with on-premises SD-WAN and SASE technologies. Integration with Cisco and Fortinet offers extended fabric and security. | Seamless interconnection, global transit between branches and Azure, optimised branch connectivity, and security. | Microsoft Docs, Azure, Cisco, Fortinet |
| 2 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:12 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:12 AM | Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Integration with Cisco SD-WAN complements AWS Transit Gateway, aiming to optimise WAN connectivity. It focuses on application optimisation, security, and cloud integration. | Secure and resilient cloud access, enhanced application performance, and efficient path selection for network traffic. | AWS, Cisco |
| 3 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:12 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:12 AM | Google Cloud | Integration with Cisco and Fortinet SD-WAN facilitates automated connectivity and on-demand provisioning, ensuring high-performance site-to-site and site-to-cloud connections. | Simplified management, automated provisioning, high reliability, and performance leveraging Google’s global cloud infrastructure. | Cisco, Fortinet |
| Cloud Vendor | Integration and Features | Key Benefits | Source |
SD-WAN optimised traffic through cloud path selection, enabling real-time network condition assessments. This dynamic selection process ensures optimal routes depending on network conditions or connection type.
The examination of these architectures is crucial in understanding how SD-WAN solutions are deployed and managed in a cloud-centric enterprise environment. Each vendor’s approach provides insights into their capabilities and outlines the strategic importance of cloud integrations. Spanning from advanced optimisation features to multi-layered security protocols, these integrations are now integral to any SD-WAN solution.
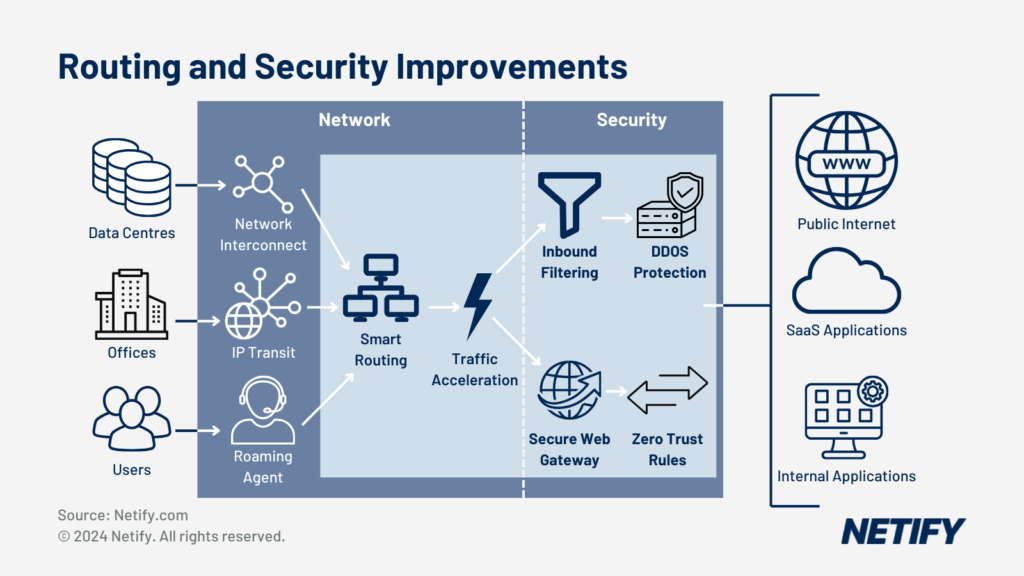
- SASE Routing and Security Improvements
Public and Private Gateways
Public SD-WAN Gateways:
Public SD-WAN gateways are provisioned on a global basis at specific PoP (Point of Presence) locations. The gateways are provisioned with multiple ISP connections to ensure resilience and diversity together with improving application performance.
Technical Characteristics:
- Multi-Tenancy: Supports multiple customers on shared infrastructure, with logical separation of traffic and robust tenant isolation mechanisms.
- Path Selection and Optimisation: Employs algorithms, which include Dynamic Multipath Optimisation (DMPO) to steer traffic based on real-time link conditions, latency, jitter, and loss.
- Cloud Integration: Native integration with IaaS and SaaS platforms, often using API-driven automation for configuration and management.
- Encryption and Security: Typically utilises IPsec tunnels for data protection, coupled with advanced end-to-end encryption standards.
Vendor Example – VeloCloud (VMware): VeloCloud’s public gateways use a multi-tenant architecture, providing cost-effective and scalable SD-WAN headend services. VeloCloud DMPO (Dynamic Multipath Optimisation) offers real-time traffic steering across multiple links and with cloud-based orchestration for centralised management. VeloCloud’s gateways also include built-in security features like stateful firewall, intrusion detection, and web filtering.
Private SD-WAN Gateways:
Private SD-WAN gateways offer an alternative to public gateways by offering MPLS and VPLS connectivity between core PoP locations.
Technical Characteristics:
- Dedicated Resources: Ensures predictable performance and capacity, free from ‘noisy neighbour’ issues common in shared environments.
- Customisable Security Posture: Allows for bespoke security configurations, including advanced firewall policies, custom IPS signatures, and dedicated VPN instances.
- Network Performance: Often integrated with WAN optimisation techniques such as deduplication, compression, and protocol optimisation for enhanced application performance.
- Private Connectivity: Direct peering with ISPs and private links, avoiding the public internet for sensitive traffic.
Vendor Example – Cato Networks: Cato provides a global private backbone, connecting Cato Sockets (edge SD-WAN devices) to Cato Cloud, a cloud-native platform merging network security with global connectivity. The architecture supports Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP) for rapid deployment and integrates a suite of security services, including next-generation firewall, IPS, and anti-malware, delivered as-a-service.
Aryaka: Aryaka’s SD-WAN solution includes a private core network with PoPs strategically placed worldwide. This setup minimises latency and optimises application performance, especially over long distances. Aryaka’s solution is also notable for their integrated WAN optimisation capabilities and the ability to provide end-to-end managed services.
Hybrid WAN
Hybrid WAN in SD-WAN architecture combines MPLS, VPLS, point-to-point circuits, and Internet VPNs. Integrated with SD-WAN, taking a Hybrid approach benefits from dynamic path optimisation and packet steering for real-time traffic routing across the best performing circuit. The optimisation feature of SD-WAN is needed to maintain performance when network conditions are impacted by packet loss or high latency.
Managing complex hybrid networks is simplified with SD-WAN, which keeps networks at optimal levels without the need to specify circuit preference. However, where needed, Policy-based control in hybrid SD-WANs allows users to set rules for path selection and network behaviours to force specific application to prefer one of the hybrid WAN circuits.
Hybrid WAN Components
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Hybrid WAN Component | Role in SD-WAN Enhancement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:15 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:15 AM | MPLS | Provides reliable, high-performance connectivity for critical applications |
| 2 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:15 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:15 AM | Broadband | Adds cost-effective bandwidth and redundancy |
| 3 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:15 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:15 AM | LTE/5G | Delivers rapid deployment capabilities and additional bandwidth |
| 4 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:15 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:15 AM | IPsec | Ensures secure connectivity over public internet links |
| Hybrid WAN Component | Role in SD-WAN Enhancement |
Managed Services
While managed services are not generally viewed as a component of the actual SD-WAN architecture, the choice of vendor or provider can impact feature capability and therefore your users.

Managed Service Provider Benefits
When selecting a managed service provider (MSP) for SD-WAN, several critical considerations must be evaluated:
- Security: The MSP should provide security monitoring to protect against cyber threats.
- Support: Continuous support and proactive monitoring are essential for maintaining network integrity.
- Service-Level Agreements (SLAs): Clear SLAs guarantee uptime, performance, and issue resolution timelines.
- Network Expansion Plans: The provider must be capable of accommodating future network growth and technological advancements.
Potential clients must ask questions to ascertain the alignment of managed services with organisational requirements:
- How does the MSP manage connectivity for Software as a Service (SaaS) and cloud infrastructures?
- What measures are in place to ensure the reliability of their managed SD-WAN service?
- Can they offer on-demand bandwidth to address fluctuating network demands?
Additional perspectives can be explored through Netify’s discussion on the purposes and advantages of SD-WAN as a managed service.
SASE Security in SD-WAN Architecture
SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) represents a more comprehensive framework that converges SD-WAN with advanced security features. SASE securely connects users, endpoints, and services regardless of their location. SASE solutions typically include a Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) model, which replaces the traditional “trust but verify” approach with “never trust, always verify.”
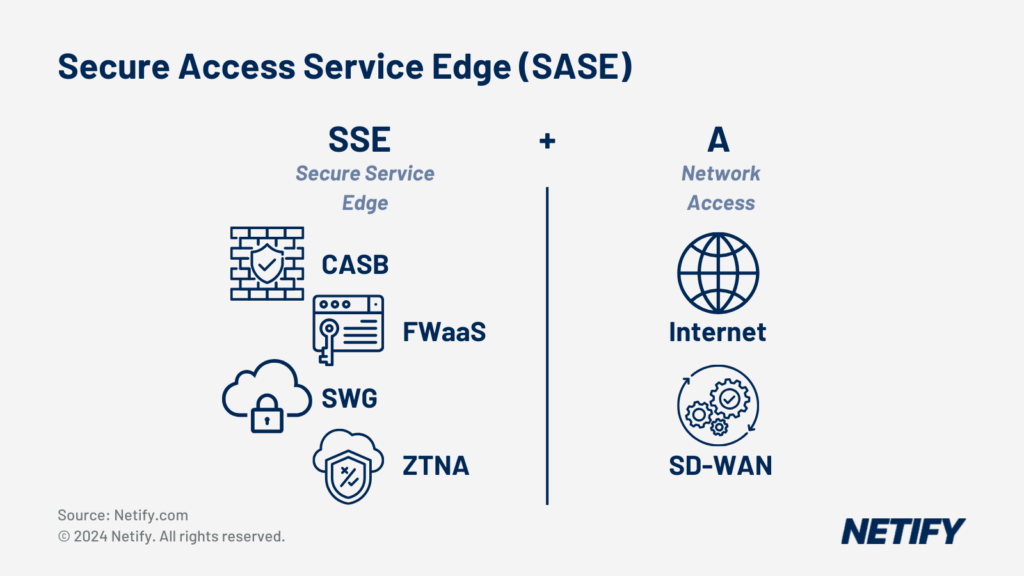
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is SSE + SD-WAN (Access).
SASE Component Functionality
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | SASE Component | Functionality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:21 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:21 AM | ZTNA | Grants secure access based on user and device identity. |
| 2 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:21 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:21 AM | MDR | Identifies and manages threats in real-time. |
| 3 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:21 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:21 AM | XDR | Provides comprehensive threat detection and response across networks. |
| 4 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:21 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:21 AM | CASB | Secures SaaS applications and cloud platforms. |
| 5 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:21 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:21 AM | SWG | Ensures safe internet access and data compliance. |
| 6 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:21 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:21 AM | NGFW | Offers advanced, granular network security. |
| SASE Component | Functionality |
In the context of SD-WAN architecture, the integration of SASE offers several advantages. SASE combines the strengths of SD-WAN, such as flexible, software-driven traffic management, with SASE’s multi-layered security. These features range from next-generation firewall (NGFW) features, secure local internet breakout, and advanced threat protection.
The move to cloud services and remote workforce models has created the need for SASE, driven by a shift towards a security model that allows organisations to support a dynamic, distributed workforce. The ability for zero-touch provisioning in SD-WAN minimises manual configurations for rapid deployment of networking and security measures across branches.
VPN connections once served as the backbone of secure remote access. But, within a SASE-enabled SD-WAN architecture, their role is more nuanced. Integrated within a comprehensive SASE framework, VPNs become part of a broader, more flexible approach to secure access.
Incorporating SASE into SD-WAN architecture is key for enterprises to achieve secure and efficient networking.
SD-WAN Architecture and AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and SD-WAN marks a transition in network management. By integrating AI, network operations are augmented with intelligent traffic management, which enables real-time access control and centralised management that is both efficient and highly capable of adapting to network demands.
Key Components of AI-Enhanced SD-WAN:
- AI: At the core of an AI-driven SD-WAN is the capability for machine learning algorithms to conduct predictive analytics, leading to informed decisions that enhance network performance.
- Automation: By harnessing AI, SD-WAN achieves a level of automation that offers rapid network configuration, reduces manual intervention, and accelerates troubleshooting.
- Network Management: AI enhances SD-WAN with sophisticated network management tools, allowing for centralised control and real-time adjustments to maintain optimal performance.
Optimisation with Machine Learning:
- Intelligent Traffic Management: ML algorithms analyse data traffic patterns to predict and mitigate network congestion before it occurs.
- Centralised Management: A centralised AI-powered dashboard provides visibility and control over the entire network, streamlining operations.
- Troubleshooting: AI-driven systems proactively detect anomalies and automate corrective actions to minimise downtime.
The integration of AI with SD-WAN extends to Internet of Things (IoT), where the vast number of devices require intelligent network solutions. Through the application of AI and machine learning, SD-WAN architectures can securely and efficiently manage IoT device connectivity.
Through advanced machine learning techniques and intelligent traffic management, AI-enhanced SD-WAN offers capabilities in network operation, troubleshooting, IoT integration, real-time access control and centralised management.
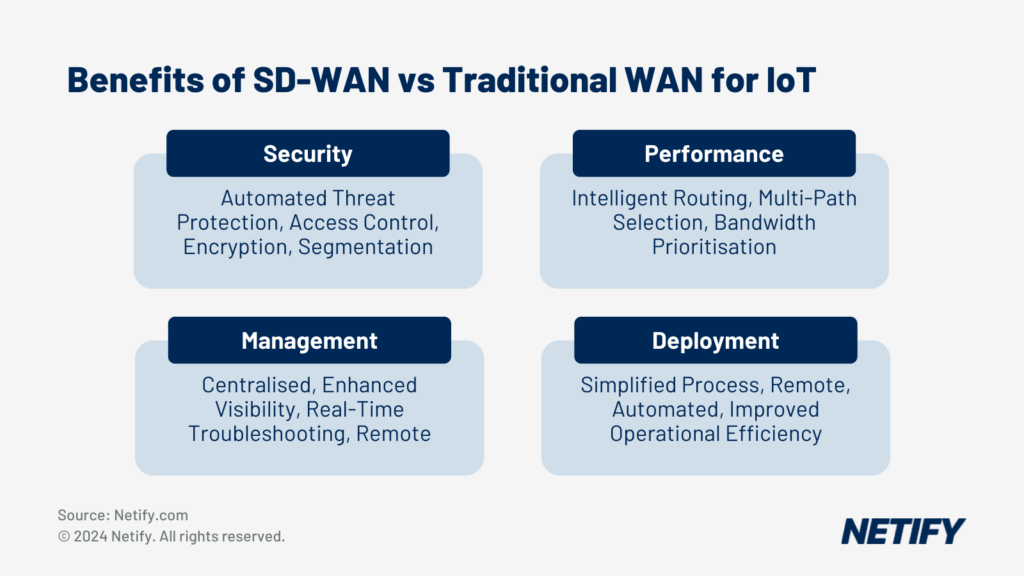
The benefits of using SD-WAN for Internet of Things (IoT)
What are the components of SD-WAN architecture?
SD-WAN Architecture Components
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Component | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | SD-WAN Edge | The network’s entry point where endpoints branch offices, remote data centres, or cloud platforms reside. It determines how data enters and leaves the system. |
| 2 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | SD-WAN Orchestrator | Serves as the network’s virtual manager, overseeing traffic flow and applying policies and protocols set by network operators. The orchestrator provides centralised operational control. |
| 3 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | SD-WAN Controller | Acts as the network’s administrative hub, responsible for centralising network management and providing operators with a single-pane view of the network. |
| 4 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | Virtual or Physical Nodes | Augment the underlay WAN. These nodes, either physical or virtual, can add additional capabilities or capacity to the existing network. |
| 5 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | Underlay Network | The existing physical network infrastructure over which the SD-WAN is implemented, such as the internet, MPLS, LTE/4G/5G, and other types of connectivity. |
| 6 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | Overlay Network | The virtual network created by the SD-WAN that sits above the underlay network. It’s where intelligent routing happens, directing traffic over the best path. |
| 7 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP) | Allows for the automated deployment and configuration of edge devices, reducing manual intervention and speeding up the deployment process. |
| 8 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | Security Functions | Integrated security features within many SD-WAN solutions, including firewalls, encryption, and intrusion prevention systems to protect the network and data. |
| 9 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | Cloud Access Points | Gateways or points of presence that allow for efficient and secure access to cloud services and applications. |
| 10 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 09:23 AM | Public and Private Gateways | SD-WAN can be delivered as site-to-site VPN or with access to public and private PoP gateways to improve global traffic performance. |
| Component | Description |


