| SD-WAN deployment strategies optimise connectivity, security, and cost, with models tailored to business needs, from DIY to managed or hybrid approaches. |
Due to the high reliance on connectivity, the capabilities of network infrastructure have become essential for business operations. Although this importance was already present through branch office connectivity, the reliance on connectivity has only been emphasised by the emergence of cloud services and remote workforces, where the reliability of the network acts as a key determinant for user productivity. In order to maximise network productivity, the infrastructure must be designed for seamless connectivity, efficient access to critical applications regardless of location, whilst protecting the network from threats.

SD-WAN Deployment Strategies
Software Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) solutions optimise network connectivity within businesses, simplify management and ensure the security of traffic across a distributed environment. Whilst SD-WAN has many features to improve the network across these key areas, it should be noted that the deployment strategy can arguably be just as important as the SD-WAN solution itself.
In this article is an outline for the different SD-WAN deployment strategies to help you, as an IT decision maker, find the best deployment approach for your unique business requirements.
Understanding SD-WAN Deployment Strategies
SD-WAN deployment strategy depends on the essential business requirements, whether it be performance optimisations, security enhancements or improved cost efficiency. Each strategy affects how the SD-WAN solution is implemented, managed and integrated with existing or legacy infrastructure.
Different types of SD-WAN architectures provide different levels of control, integrations with the cloud and on-premises appliances, therefore it is important for IT decision makers to be aware of these factors prior to choosing a solution, It is also essential to consider planned changes of organisation size, current network administrator knowledge, budgets and security requirements or regulatory compliance, as these factors may also affect the suitability of different solutions.
SD-WAN Deployment Requirements and Integrations
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Business Requirement | SD-WAN Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 12:58 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 12:58 PM | Performance | SD-WAN enables efficient traffic routing, prioritisation of applications and adaptability for changing network conditions. |
| 2 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 12:58 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 12:58 PM | Security | SD-WAN offers features such as segmentation, encryption, anti-malware and intrusion prevention systems for preventing breaches. |
| 3 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 12:58 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 12:58 PM | Reduce Costs | SD-WAN can leverage multiple transport links, utilising cost-effective broadband and cellular networks in order to reduce the reliance on dedicated MPLS which can be expensive. |
| 4 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 12:58 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 12:58 PM | Simplify Management | SD-WAN provides a centralised management pane where operations can be automated, orchestrated and provider faster troubleshooting for network administrators. |
| 5 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 12:58 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 12:58 PM | Scalability | SD-WAN ensures the network can be easily expanded, often integrating cloud service OnRamping and the ability to adapt to changing business requirements. |
| Business Requirement | SD-WAN Implementation |
Key Considerations Before Deployment
By evaluating the existing network, businesses can determine where network infrastructure may be difficult to integrate, such as legacy systems. Performance factors such as bandwidth limitations and network congestion should be considered, alongside potential security vulnerabilities. These are important for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity and availability of the network.
For growing business requirements, SD-WAN solution that can scale its user base, enabling business expansion, ensuring application performance is not affected and compliance with business security regulations.
Where remaining within budget restraints is of greater importance, SD-WAN reduces reliance on expensive dedicated MPLS by leveraging multiple transport links such as cost-effective broadband.
Through simplified network management and Artificial Intelligence (AI) automation, the workload for network administrators is reduced. With the help of external consultants and Managed Service Provider (MSP) support, technical expertise requirements can be reduced. Where businesses are considering utilising a DIY approach to SD-WAN but do not yet have the in-house expertise, it is advisable that administration training and certifications are attained prior to deployment.
For businesses with a focus on sustainability, the energy efficiency of the network should be considered. By consolidating the network infrastructure, organisations can reduce the carbon footprint of their network hardware. SD-WAN also enables cloud migration, reducing the reliance on individual dedicated data centres for businesses.
If being reliant on a single vendor (vendor lock-in) isn’t your thing, it’s important to evaluation SD-WAN solutions based on their interoperability, by running proof-of-concept trials across multiple vendors. Another approach is to negotiate flexible contract terms and exit clauses, enabling a switch of vendor should interoperability become an issue in the future.
Deployment Models for SD-WAN
Once you have considered your key criteria, choosing the appropriate SD-WAN deployment model for your network can be the difference between a fully optimised network and a complicated problem to troubleshoot. The three primary deployment models for SD-WAN are Do-It-Yourself (DIY), managed and hybrid.
Within DIY models, an organisation’s in-house network administrators are solely responsible for designing, implementing and managing the SD-WAN solution. This requires the network administration team to either have previous skill in SD-WAN or be provided training in order to get the most out of the solution.
SD-WAN Deployment DIY Pros and Cons
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:06 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:06 PM | Full control over the network architecture. | Requires in-house expertise to deploy and maintain. |
| 2 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:06 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:06 PM | Complete policy management. | Requires dedicated resources for monitoring and troubleshooting. |
| 3 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:06 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:06 PM | Ability to customise solution based on organisation requirements. | |
| 4 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:06 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:06 PM | Potential cost savings by leveraging pre-existing resources. | |
| Pros | Cons |
For managed SD-WAN, organisations outsource the deployment, management and support via a third-party provider, MSP or systems integrator. This hands over control of the network to a third-party, minimising your network administrators from requiring expertise, but does come at the expense of being entirely dependent on the provider.
SD-WAN Deployment Managed Pros and Cons
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:09 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:09 PM | Reduces complexity and overhead for administrators. | Dependent on the service provider to make network changes or troubleshoot issues. |
| 2 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:09 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:09 PM | Specialised expertise from service provider assists with troubleshooting. | Often comes at a higher cost to DIY solutions, depending on the scope of services. |
| 3 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:09 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:09 PM | Improved network performance and reliability through dedicated monitoring and management. | Grants organisations less control over the network architecture and policy management. |
| Pros | Cons |
Alternatively, hybrid SD-WAN models combine elements of both DIY and managed SD-WAN, providing a balance of control and outsourced expertise. With hybrid SD-WAN, network administrators work closely with an MSP in order to design and implement the network. This is commonly seen as a ‘best-of-both-worlds’ approach but does require constant communication between internal and external teams to prevent network goals from becoming misaligned.
SD-WAN Deployment Hybrid Pros and Cons
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:10 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:10 PM | Maintain control over critical components whilst leveraging external expertise. | Can create additional overhead to align internal and external administration. |
| 2 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:10 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:10 PM | Ability to customise solution based on organisation requirements. | Can increase complexity due to vague delegation of responsibilities between internal and external administration. |
| 3 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:10 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 01:10 PM | Potential to optimise cost efficiencies by leveraging a mix of in-house and outsourced services. | |
| Pros | Cons |
Implementation Phases
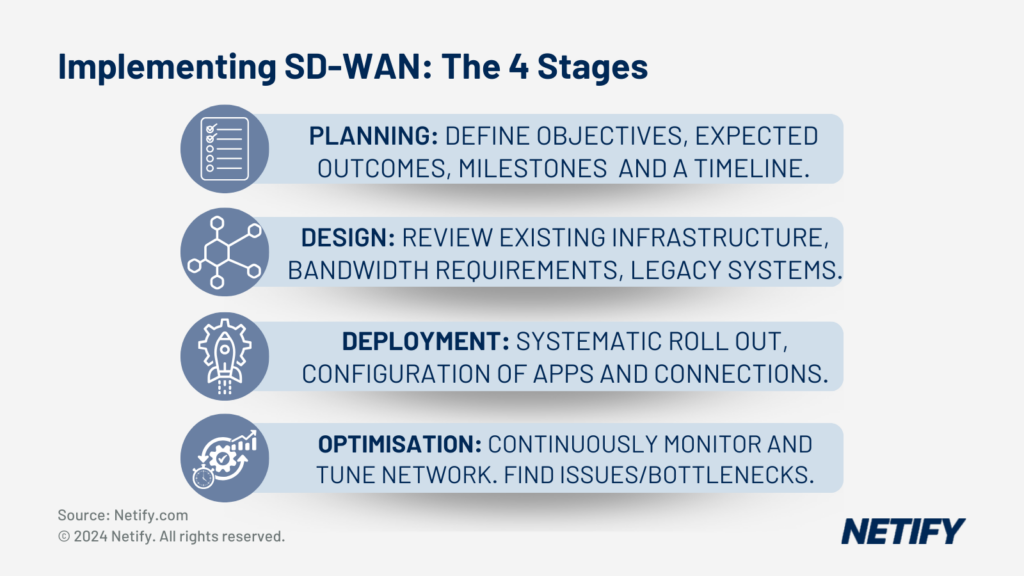
The 4 Stages of Implementing SD-WAN
The first phase is planning. This phase consists of setting clear objectives and detailing the expected outcomes, e.g., improve network performance, enhance security, reduce costs, enable cloud connections. These objectives can then be turned into milestones and chronologically aligned into a timeline, stating the resources that must be allocated to each stage.
Secondly, the design phase requires review of network architecture design based on organisation requirements, existing infrastructure and future growth expectations. Design factors such as network topology, bandwidth requirements and integration with existing/legacy systems.
When deploying the SD-WAN, network administrators must take a step-by-step, systematic roll out of the network. Pre-deployment techniques include network emulation and simulation tools, traffic generation and load testing, application performance monitoring, security vulnerability scanning. These techniques enable the configuration of applications and connections to be established within a controlled environment, easing the migration of applications and services. By pilot testing within a controlled environment, it allows network administrators to validate configurations and identify potential flaws, such as unexpected latency. A gradual roll out of the system across other sites allows thorough testing and the ability to see how the SD-WAN solution copes with network scaling.
Finally, the optimisation phase requires network administrators to continuously monitor and tune the performance of the network. Through monitoring, network administrators can find potential bottlenecks, latency issues and security vulnerabilities. This can often be seen as an ongoing phase due to the constant need to continuously monitor the network in order to maintain optimal performance.
Best Practices for Successful SD-WAN Deployment
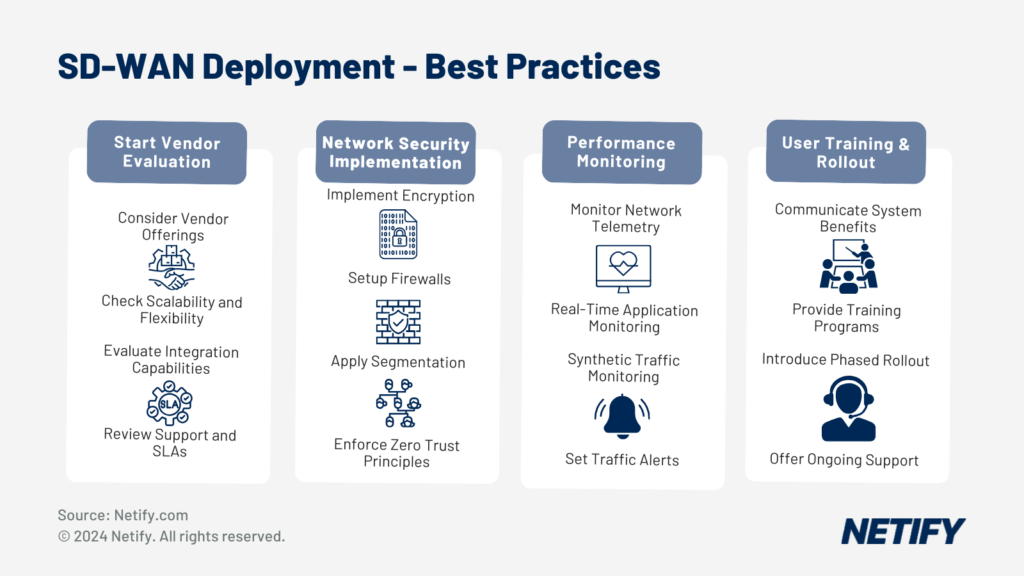
Best Practices for Successful SD-WAN Deployment
For successful SD-WAN deployment, IT decision makers must consider the vendor offerings. This is important due to each vendor offering differing features, varying levels of scalability/flexibility and integration capabilities. Vendors may also offer support or Service Level Agreements (SLA) as part of their SD-WAN solution, which may assist specific business requirements. To better understand SD-WAN vendor offerings, we would recommend taking a look at our SD-WAN comparison article.
When deploying SD-WAN, network administrators may wish to implement network security features such as encryption, firewalls, segmentation and zero trust principles. These features protect the network from potential breaches, improving the confidentiality and integrity of network traffic.
By monitoring network telemetry, administrators can determine if the SD-WAN solution provides the required performance. Telemetry can be monitored in several ways, with real-time application performance monitoring, synthetic traffic monitoring and through traffic alerts.
Finally, arguably the most important factor for successful SD-WAN deployment is user training. By communicating the system benefits to stakeholders, providing training programs to administrators and introducing a phased rollout with ongoing support, organisations can ensure that they get the most out of their SD-WAN solution, with network administrators being capable of managing the SD-WAN without issue.
Common Challenges and Solutions
One common challenge for organisations when implementing SD-WAN is the integration with existing network infrastructure. This can be particularly true for complex legacy systems, where multiple vendors are used, or a diverse network architecture is already being leveraged. To mitigate this issue, IT decision makers should first identify potential compatibility issues and requirements as part of the design phase and vendor evaluation. By taking a phased integration approach, this minimises the potential disruptions to business operations and enables localised validation of interoperability on existing hardware, software and network protocols. Where pilot testing is harder to conduct, it may be preferable to closely collaborate with a vendor, enabling issues with converging existing hardware and SD-WAN to be addressed prior to integration roll out.
Another challenge is that the SD-WAN solution requires scalability. For businesses where the network is rapidly expanding, it may be advisable to invest in a more modular architecture. This enables swapping components in and out to meet the demands of the business at any given scale. One example of this is cloud-ready SD-WAN, which enables seamless cloud integration for a hybrid approach. This means that businesses can utilise the cloud for a growing number of users and applications, provides automated provisioning and reduces the requirements to reinvest in on-premises appliances to cope with a growing network.
When transitioning to a new form of network infrastructure, network administrators may find it difficult to adapt to the management complexity of SD-WAN. This is due to the distributed environment, ability to leverage multiple transport links and advanced security features. The management complexity can be reduced by factors such as reducing workload for network administrators (using a central management system, automated orchestration processes, standardised policies/processes) and through upskilling network administrators.
Future Trends in SD-WAN Deployment
Cloud-first strategies are increasingly being leveraged within SD-WAN. Cloud-first is a strategic choice to primarily utilise cloud resources, with alternative options used as a fallback or redundancy. This has emphasised the need for solutions such as cloud-native SD-WAN and SD-WAN supporting multi-cloud.
Cloud-native SD-WAN enables faster development and deployment by reducing the need for on-premises appliances to be delivered.
By leveraging the cloud through SD-WAN, it enables elastic scaling for optimised performance and cost efficiency, which when combined with multi-cloud, allows businesses to combine the benefits of different cloud providers (such as AWS, Azure and GCP), whilst minimising costs for each.
SD-WANs are leveraging AI and machine learning to optimise network performance, automate tasks and enhance security monitoring. This will improve overall network performance and increase reliability.
There has also been an uptake in Edge computing, which processes data closer to the source of the network connection. Through a reduction in data transmission, edge computing enables the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices with SD-WAN and provides bandwidth optimisations whilst ensuring security at the network edge.
Conclusion
The deployment of SD-WAN enables businesses to enhance their network performance, scalability and security, improving the availability, integrity and confidentiality of network resources and traffic. By carefully planning the integration phases, selecting the correct SD-WAN vendor and using a step-by-step roll out of the integration, organisations can reduce the amount of issues they experience.


